-
ESPP
-
Alignment with ESG Frameworks
-
Key Sustainable Initiatives
-
Waste Management
-
Stakeholders Consultation
-
Efforts Towards Mitigating Climate Change
-
Disclosures
Environment and Social Policy Statement
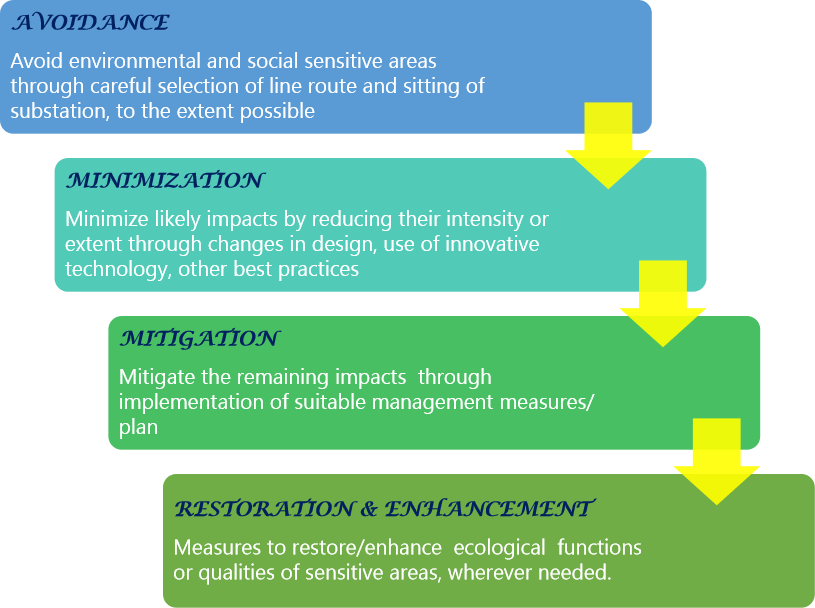
"POWERGRID is committed to the goal of sustainable development and conservation of nature and nature resources. While continually improving its management system, accessing specialist knowledge and introducing state of the art and internationally proven technologies, POWERGRID strictly follows the basic principles of Avoidance, Minimization and Mitigation in dealing with environmental and social issues. Where necessary, restoration and enhancement is also undertaken"
Major Milestones
-
1998
ESPP Developed & Its implementation started across POWERGRID
-
2005
1st updation of ESPP in line with changed rules and guidelines including that of multilateral funding agencies
-
2009
2nd updation of ESPP to make it compliant with the World Bank’s Use of Country System (UCS) Policy
-
2010
First Indian PSU in Power Sector to disclose a standalone Sustainability Report for FY 2008-09
-
2017
ADB approved POWERGRID ESPP as its first document in Asia under Country Safeguard System (CSS).
Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures (ESPP)

- Developed in 1998 and further updated in 2005 & 2009.
- Evolved through broader consultation process at National, Regional and Site level involving all major stakeholders.
- Follows the basic principles of Aviodance Minimization & Mitigation to address E & S issues associated with transmission line projects.
- Provisions mostly aligned with the policies/ standards of major multilateral of agencies like The World Bank, The ADB etc as well as international best practices,
- Mandatory provisions of project specifc E & S Assessment / EMP, study of alternatives, public consultation & public disclosure of safeguard document etc. go beyond the National Requirements.
SOCIAL OBJECTIVES
- Follow prescribed precautions to minimize disturbance to habitation, tribal areas and places of cultural heritage
- Consult/involve Affected Persons/communities during all stages of project implementation
- Special attention to marginalized and vulnerable groups and secure their active participation
- Maintain highest standards of health and safety to avoid possible accidents
ENVIRONMENTAL OBJECTIVES
- Avoid operations in environmentally sensitive areas, eco- sensitive zones, forests, sanctuaries, national parks, tiger/biosphere reserves, and coastal areas covered under CRZ through study of alternatives
- Consider/design innovative/practical engineering/biological solutions by considering environmental implications of project implementation
- Application of efficient and safe technology practices
- Abate pollution in all activities and operations
- Minimize energy losses and promote energy efficiency
Continuing our Sustainability journey started in year 1998 with the disclosure of our ESPP and to provide further impetus to it, POWERGRID has started the process of ESG framework. This has been necessitated not only due to the fact that the contours of the business and market dynamics are changing but also to fulfil the rising expectations of our stakeholders.
Since, we want to be a part of the solution of the pressing problems of the world such as climate change, ESG framework will help us in synchronizing and consolidating our sustainability efforts and bring more transparency in our reporting processes. Additionally, it will be also useful in complying with the newly introduced regulatory requirements such as “Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report” by the Stock Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
POWERGRID has aligned its business activities with 13 SDGs out of total 17.
Partnering with Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), South Asia for United Nation's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Agenda 2030.

Natural Resource Management
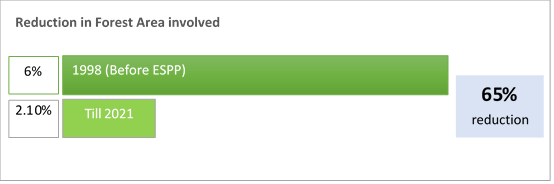
Following the basic principles of resource efficiency through Avoidance and Minimization, involvement of forest, an important natural resource/carbon sink, has been progressively reduced by around 65 % from a baseline of 6 % in 1998 through route optimization by including study of alternative routes and use of modern survey tools.
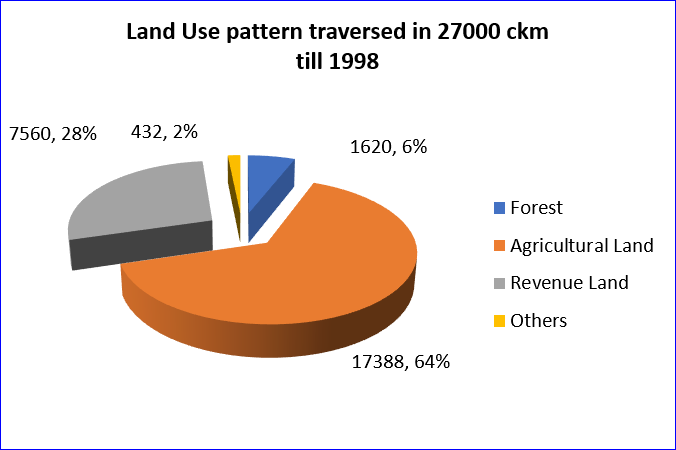
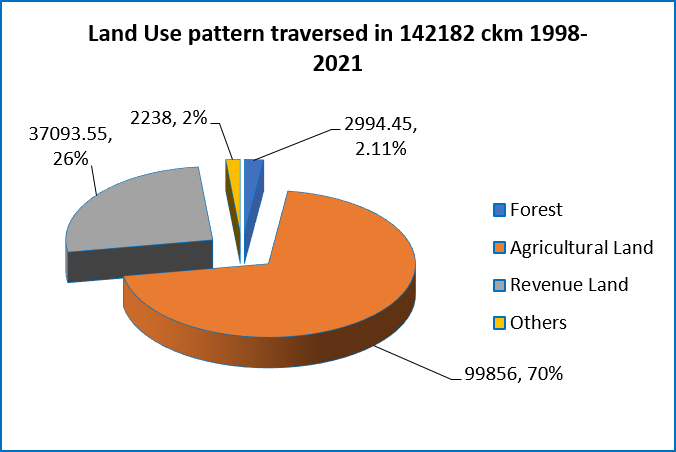
Leveraging modern technology in the form of development & use of innovative tower design (multi-circuit, compact and pole type towers) and adoption of high voltage levels transmission system (1200 kV, ±800kV HVDC, 765kV etc.) not only reduce the requirement of precious land resources and social risks to projects but also substantially reduce felling of tree as well as conservation of wildlife in ecologically sensitive areas




Reducing Social Impacts
Minimizing social impacts through land optimization, adoption of compact substation (GIS) in place of conventional AIS, locating substation primarily on encroachment free barren Govt. land.


Securing land for substation through “Willing Buyer Willing seller” basis on market/negotiated rate to ensure mutually beneficial stakeholder relation and to avoid public resistance/court intervention.
Replenish Natural resources



Massive plantations with suitable indigenous species with more than 7 Lakh trees in its establishments till 2021. Additional, 5.5 lakh plantation planned by 2030
Rain Water Harvesting, an integral and mandatory part of our substations’ design with an aim to conserve precious rainwater and sustainability of ground water aquifers through harvesting / recharge.
No major solid or liquid waste generated due to very nature of our activities except metal scraps, used batteries, transformer oil and e-waste etc. which are disposed of in environmentally sound manner to authorized recyclers/reprocessors or channelized back to manufacturers for recycling following applicable regulations. For other wastes like domestic organic waste, paper etc. generated from day to day activities our waste management program is based on reduce, reuse and recycle principle. Followings are some key initiatives undertaken by POWERGRID

Installation of composting machines at more than 55 locations for recycling and reuse of organic/bio-degradable waste generated from its residential townships/substation and office establishments. This initiative has eliminated the problem of disposal of organic waste as well as compost produce from such waste is gainfully utilized inhouse.

Established a “Waste Paper Recycling” plant at Gurgaon Substation with capacity to handle 40-60 kgs of waste paper daily that has resulted in conservation of natural resources like tree, water etc. and also reduced procurement of paper/stationary items from the open market.
Digital initiatives towards paperless work such as e-office, DREAMS (Drawing Review and Engineering Approval Management System), e-Tendering Portal-PRANIT, establishment of Centralized Vendor Bill Processing facilities etc. has not only reduced the generation of waste paper substantially but also paved the way for paperless office in future.
POWERGRID ensure that all our stakeholders from government departments, communities to individual landowners and employees are well informed, involved and fully understand the role of POWERGRID in transmission of power across the country. The ESPP spells out its commitment to ensure total transparency through a well-defined public consultation process as well as dissemination of relevant information about the project at every stage of its implementation.
During formal and informal consultations, questions/doubt/queries of community are heard and answered to their satisfaction. We also encourage members of public to put forward their feedback/suggestion which in turn, as per feasibility are considered during various stages of project implementation. This process not only ensures a feeling ownership towards project among the local community but also greatly enhances the image of the organization.




Towards fulfilment of GoI’s target of 500 GW Capacity from non-fossil energy sources by 2030, POWERGRID is playing a pivotal role for grid integration of various Renewable Energy Zones in the country through implementation of high capacity Green Energy Corridors (GEC).
Recognizing the importance of renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint, POWERGRID has already installed 7.6 MWp of rooftop Solar PV systems at 118 locations. Further, Installation of 7.5 MWp at 96 locations is in process of planning/ implementation. Established capacity of rooftop solar PV systems is reducing about 9300 MT of CO2 emission annually.
POWERGRID is also evaluating setting up solar generation plants on vacant land available in substations. First of such plant to be established in Nagda, (M.P.) having 105 MWp capacity.

Pioneering effort in developing technology for use the inductive power in earth wire for powering of telecom antennas has huge potential to reduce emission of Green House Gases (GHGs) from DG sets -a constant source of pollution and GHGs emission. This initiative will result in saving of 40-60 tCO2/ year/location.
On Climate resilience front, POWERGRID has taken initiatives viz. strengthening of towers in areas with changing wind profiles, hardening design parameters etc. to combat climate change risks to our assets.
Increasing the carbon sink through plantation of suitable species in all its establishment with a target to plant 5.5 lakhs more trees by 2030 in addition to 7 Lakh trees already existing.
North Eastern Region Power System Improvement Project (NERPSIP)
Safeguard Documents
- Land Registry
- 1st E & S Safeguard Monitoring Report December 2018
- 2nd E & S Safeguard Monitoring Jan-June 2019
- 3rd Semi-Annual E & S Safeguard Monitoring Report July-Dec 2019
- 4th Semiannual E & S Safeguard Monitoring Report Jan-June 2020
- 5th Semi-Annual E & S Safeguard Monitoring Report
- 6th Semi-Annual E & S Safeguard Monitoring Report January-June 2018
- EMP in Assamese
- EMP in Bengali
- EMP in Manipuri
- EMP in Mizo
- Entitlement Matrix and Public Consultation in Manipuri
- Entitlement Matrix and Public Consultation in Assamese
- Entitlement Matrix and Public Consultation in Bengali
- Entitlement Matrix and Public Consultation in Mizo
- ESPPF Executive Summary Manipuri
- ESPPF Executive Summary Assamese
- ESPPF Executive Summary Bengali
- ESPPF Executive Summary Mizo
Assam
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Dhemaji District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Tinsukia and Dibrugarh District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Golaghat, Nagaon, Jorhat, Sibsagar and Karbi Anglong District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Kamrup Metropolitan District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Kamrup Rural, Udalguri and Sonitpur District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report 33 kV UG Cable laying works in Guwahati City
- CPTD for T&D in Dhemaji District
- CPTD for T&D in Tinsukia and Dibrugarh District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Golaghat, Jorhat, Nagaon, Sibsagar and Karbi Anglong District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Kamrup Rural, Udalguri and Sonitpuri District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Dhemaji District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Dibrugarh and Tinsukia District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Golaghat, Jorhat, Nagaon, Sibsagar, Karbi Anglong, Hojai and West Karbi Anglong District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Kamrup Rural, Udalguri, Sonitpur and Nalbari District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Kamrup Metropolitan District
Meghalaya
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report - West & South-West Garo
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report - East Jaintia Hills District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report - East Khasi & Ri-Bhoi District
- CPTD for T&D in West & South Garo Hills District
- CPTD for T&D in East Jaintia Hills District
- CPTD for T&D Network in East Khasi Hills & Ri-Bhoi District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Garo Hill District
- FEAR for T&D Network in East Khasi Hills and Ri-Bhoi District
- FEAR for T & D Projects in East Jaintia Hills District
Tripura
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Gumti and South Tripura District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Dhalai, Unakoti and North Tripura District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report West Tripura, South Tripura, Khowai and Sephijala District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Additional Scope in West Tripura District
- CPTD for T&D in West Tripura, South Tripura Khowai & Sepahijal District
- CPTD for T&D in Dhalai, Unakoti and North Tripura District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Gumti and South Tripura District
- FEAR for T&D Networks in West Tripura, South Tripura, Khowai & Sepahijala District
- FEAR for T&D Networks in Dhalai, Unakoti & North Tripura District
- FEAR for T&D networks in Gomati & South Tripura District (FEAR-II)
- FEAR for T&D Networks in Gomati & South Tripura District (FEAR-III)
- FEAR for T&D Network in Gomati & South Tripura District (FEAR-IV)
Manipur
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Imphal West, Senapati and Bishnupur District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Imphal East, Churachandpur, Thoubal and Tamenglong District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Imphal West Imphal East & Tamenglong District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Imphal East, Churachandpur, Thoubal & Tamelong District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Imphal West, Imphal East & Tamenglong District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Imphal West, Senapati & Bishnupur District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Imphal East and Tamenglong District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Imphal East, Churachandpur, Thoubal and Tamenglong District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Imphal West, Senapati and Bishnupur District
Mizoram
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Lunglei & Lawngtlai District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report for T&D Network in Mammit District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Lunglei & Lawngtlai District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Mammit District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Lunglei & Lawngtlai District
- FEAR for T&D Network in Mammit District
Nagaland
- Environmental and Social Policy & Procedures Framework
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Tuensang And Longleng District
- Initial Environmental Assessment Report Mokokchung, Kohima, Phek, Wokha, Zunheboto, Dimapur, Mon District
- FEAR of Mokokchung, Kohima, Phek, Wokha, Zunheboto, Dimapur, Mon District
- FEAR Tuensang and Longleng District
- CPTD for T&D in Mokokchung, Kohima, Phek, Wokha, Zunheboto, Dimapur & Mon District
- CPTD for T&D Network in Tuensang and Longleng District